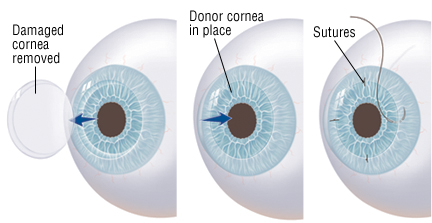
Corneal transplantation, when indicated, can help to restore functional vision in an eye with corneal damage. However, like all surgeries, there is risk that must be balanced against the degree of difficulty the patient is experiencing as a result of his or her corneal disorder.
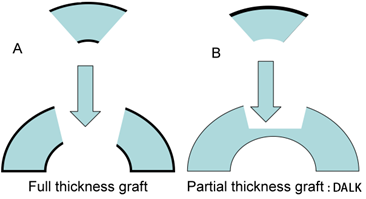
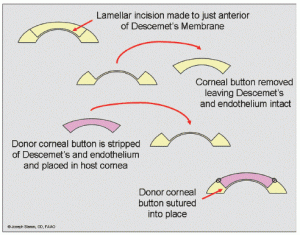
Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty (DALK) can be a good option to consider when the innermost layers of the cornea are healthy, but the front most layers of the cornea are the problem. Common indications for this DALK_lgprocedure include keratoconus and corneal scars. In DALK, the patient’s inner corneal layer (the endothelium) is left intact and all other layers of the cornea are removed. The donor cornea is prepared and the endothelium removed. The donor tissue is then sutured into place over the recipient’s own endothelium. There are a few potential benefits with DALK: fewer postoperative complications, less incidence of rejection, and shorter use of topical steroid treatment.
A common threat to the success of a corneal transplant is graft rejection. Rejection occurs in about 10% of cases of traditional Penetrating Keratoplasty (PK). Rejection most commonly arises from the donor endothelium. The other layers of a transplanted cornea are much less likely to incite rejection. In DALK, a person’s endothelium is left intact and this lowers the incidence of rejection.
As in traditional PK, Sutures are used to hold the donor corneal tissue in place during the recovery period. Occasionally, the sutures can become loose, which may result in infection or induce astigmatism. It is impossible to predict the glasses prescription that will result after a corneal transplant. It is common for a significant amount of far sightedness, near sightedness or astigmatism to be present following a full-thickness corneal transplant. In some cases, the prescription is strong enough that eyeglasses alone cannot offer adequate vision or balance with the other eye. For these individuals, contact lenses, or additional surgery, may help to bring the eyes into focus and balance.
Corneal transplants are vulnerable to traumatic injury that may result in rupturing the eye (even years after the original transplant) because the transplant never heals as strong as a normal cornea. Therefore, extra caution and some restrictions are required for life after undergoing corneal transplantation, which must be considered prior to surgery. Typically, the visual recovery time following a full-thickness transplant is one year. During this recovery period, patients are monitored closely to ensure normal healing and adjust sutures if needed to optimize the visual outcome. It is recommended that a patient with a corneal transplant call promptly if there is pain, blurred vision, light sensitivity or redness as this may represent a broken suture, infection or graft rejection in need of treatment.


